
Decorative electroplated chrome coatings on plastics have been produced for decades. For environmental reasons, there has been a shift away from hexavalent chrome (Cr6) to trivalent chrome (Cr3). Interest in alternatives to electroplated chrome is expanding dramatically. The process steps of applying chrome and other metal coatings to plastic are very different when comparing electroplating and physical vapor deposition (PVD). In electroplating, numerous chemical baths and rinses are required to deposit 15 to 30 microns of metal for producing a durable chrome appearance. Electroplating processing steps are well known and can include conditioning, neutralizing, acid etching, catalyzing, accelerating, nickel flash, copper plating, nickel plating, chrome plating, and effluent care and disposal. For this reason, there are increasing investments towards elemental chrome PVD coatings to maintain the true chrome appearance. Collectively, the automotive, home appliance and cosmetic markets are actively searching for alternatives with the appearance and durability of electroplating, but without the environmental side effects, appearance and functional design limitations, and costs associated with it. Finishers have been looking to focus on a safer, greener, more cost-effective, quicker alternative without sacrificing appearance and performance.
Traditional chrome plating is limited to coating-grade substrates like acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and polycarbonate/ABS. Certain thermoplastics, like polyamide/polyphenyl ether, cannot be chrome plated due to either chemical attack or the duration in high-temperature baths (up to 140 °F for 11 min) causing substrate deformation.
ABS has been widely used as a substrate for vacuum deposition and electroplating since the 1960s. The material is relatively inexpensive and can be easily injection molded, but for most applications where the part is directly exposed, or viewed through a clear lens, a base coating (of paint) to smooth the surface of blush and flow lines prior to vacuum deposition has been required. A more expensive plating-grade ABS is used for components to be electroplated. PVD processing has greatly opened up the materials that can be directly coated including: ABS with polycarbonate blends, polyamide, polyetherimide, polybutylene terephthalate, polystyrene and others.
In this article special emphasis is given to PVD technology and its application for polymeric materials in the automotive and home appliance industries, highlighting cost reduction and improved quality around surface modification of parts.
The application of PVD techniques ranges over a wide variety of applications from decorative to high-temperature superconducting films. A very large number of inorganic materials - metals, alloys, compounds and mixtures - as well as some organic materials, like polymers, can be deposited using PVD technologies. Nowadays, PVD is used to form multilayer coatings, radiant depositions or very thick deposits.
PVD is the deposition of a metal onto a substrate through changes in the physical state of the metal (solid to gas to solid). When used in conjunction with a UV coating process, a basecoat is applied to the substrate, a very thin layer (700-1000 angstroms) of metal is deposited, and then encapsulated by a UV topcoat to seal and protect the underlying layers (Figure 1). To understand how thin the layer of PVD actually is, consider that a typical UV coatings thickness for PVD applications is 25 microns or 0.98 mil. 1.0 mil is 25,400 nanometers. An angstrom is described as one hundred millionth of a meter, or 10-10 or 0.1 nanometers.
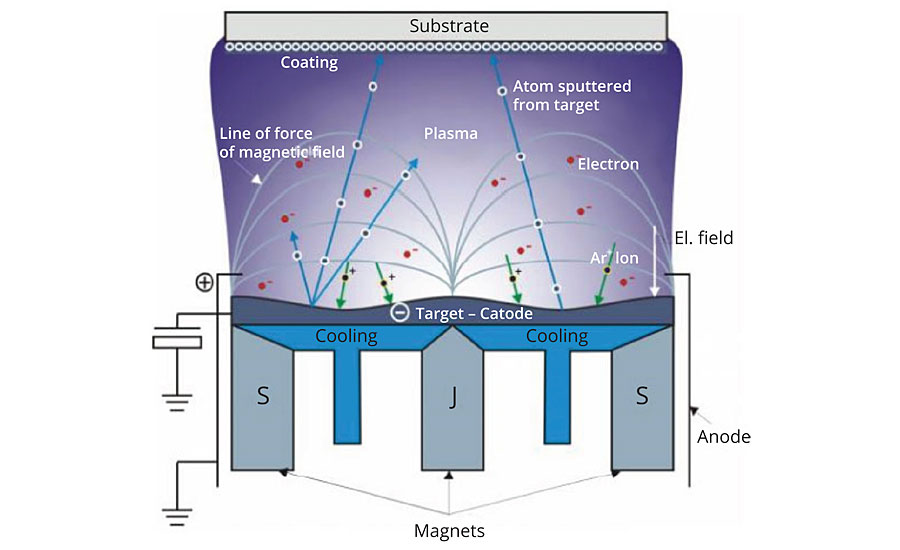
FIGURE 1 ? The PVD coating process.
With PVD, a wide variety of metals can be deposited including aluminum, chromium, titanium, stainless steel, nickel chrome, tin, etc. The PVD layer can be deposited by a variety of methods, including, but not limited to, thermal evaporation, cathodic arc, sputtering, pulsed laser deposition and electron beam deposition. The common method we will focus on is sputtering deposition that is done in a vacuum.
Sputtering is the deposition process where atoms on a solid metal target are ejected into a gas phase due to bombardment of the material by high-energy ions. The bombardment releases atoms from the metal target, which are deposited directly onto the part within the vacuum chamber. Metal thickness will vary depending on the cycle time and power applied to the target.
When evaluating PVD coating and electroplating, different test methods were performed on different stages and types of ABS substrates to optimize the circumstances. Test methods are described in Table 1.
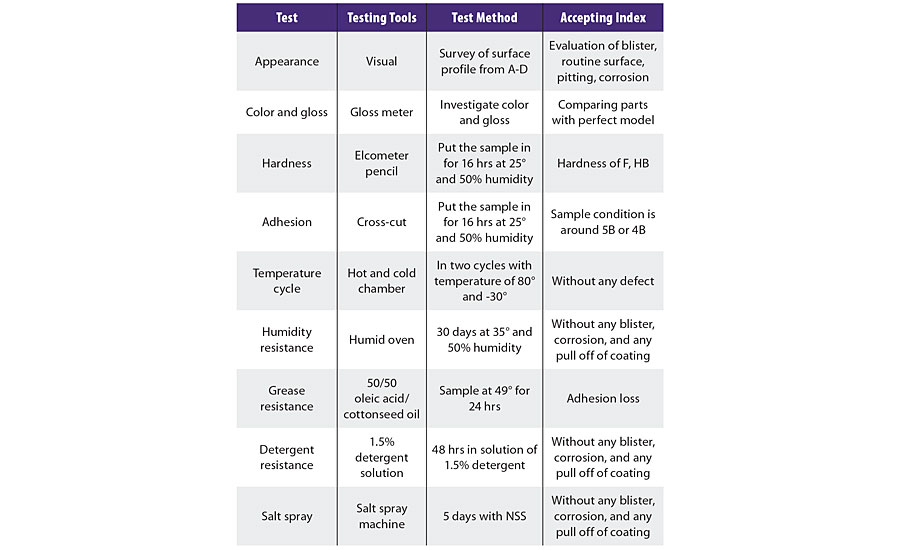
TABLE 1 ? Test methods.
Acids and Alkalis
When visually checking a PVD or electroplated sample there are some points that should be noted in regards to testing with acids and alkalis.
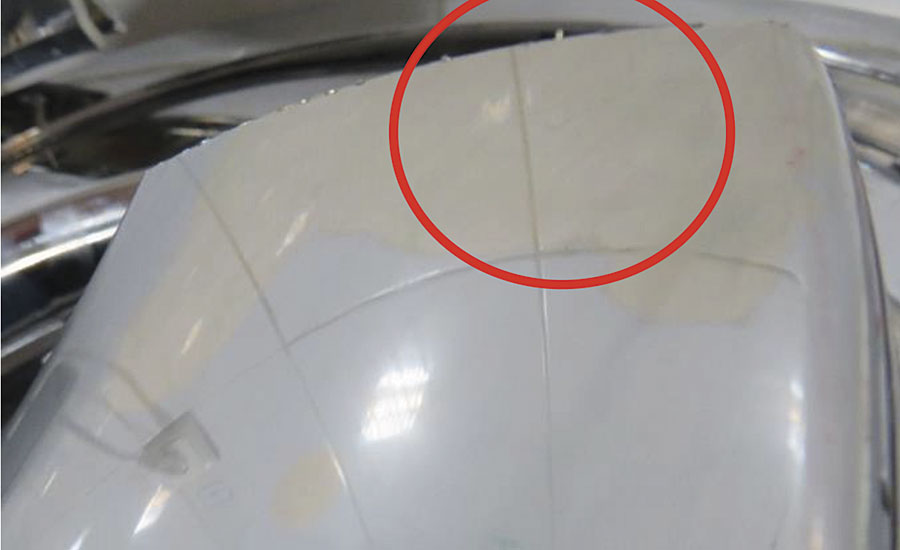
A sample coated with a PVD system with aluminum target can be tested with acid and there is no defect on the coating, but when this test is conducted with soluble alkalis some defects and damage result, as can be seen in Figure 2.
When a sample that is coated with a traditional electroplated system encounters acid, the chrome coating vanishes and the yellowish color of nickel promptly appears. This result is shown in Figure 3.

Adhesion and Hardness Testing
The cross-cut method was used to test adhesion and hardness on a PVD-coated ABS plastic substrate (Figure 4a). The adhesion and hardness of the PVD specimen can be interpreted based on the schematic in Figure 4b.
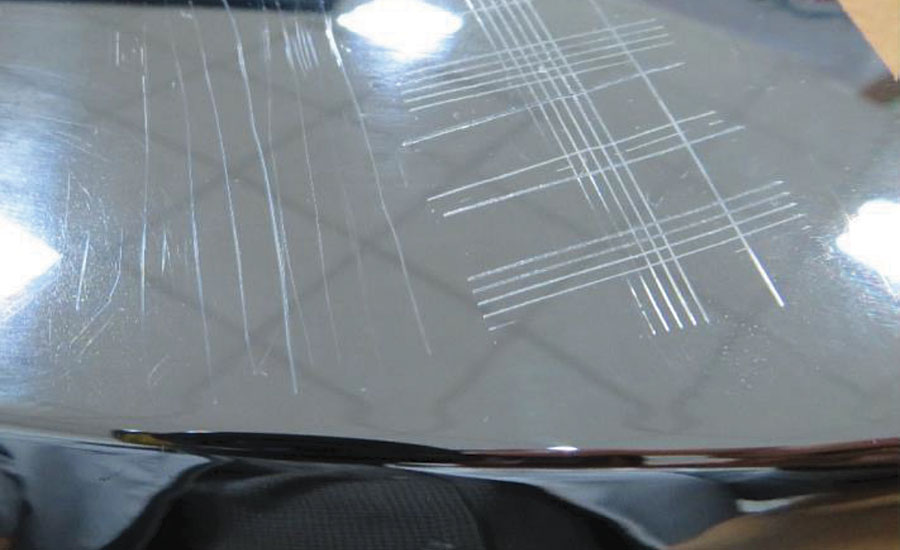

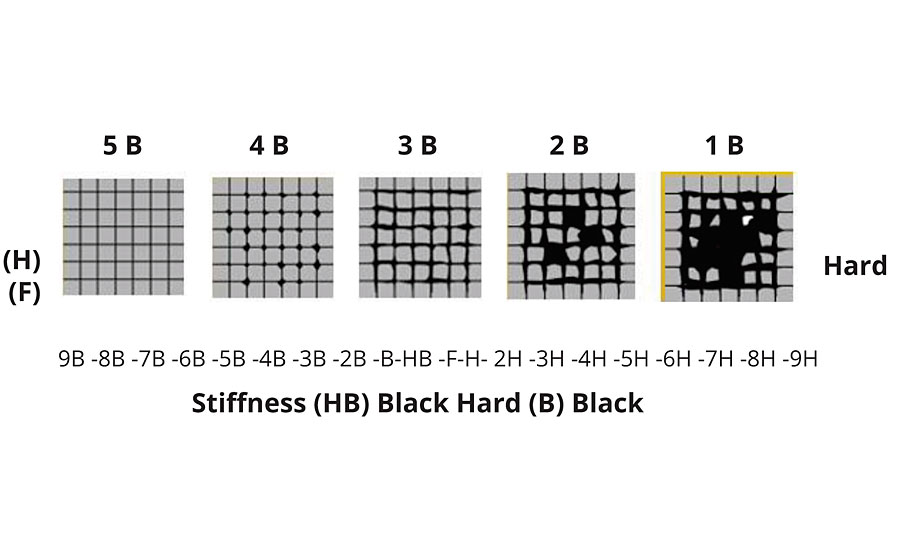
The adhesion of the coating on ABS substrates was 5H. The hardness of the PVD coating was HB-1.5N and the chrome plated was 2B-0.5N.
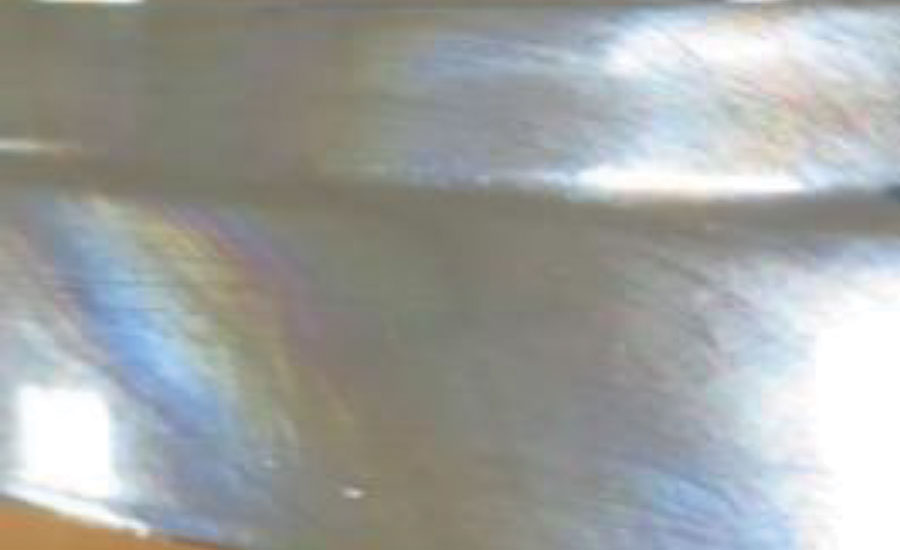
Adhesion was also evaluated with thermal cycles in different temperatures ranging from 80 °C to -30 °C. The test showed that according to the standards, PVD coating with aluminum target cannot achieve positive results in different categories of adhesion testing. The specimen was put in hot and cold chambers in different thermal cycles for 1 hr at 20 ±3 °C and for 30 min at 20 ±3 °C. During the test, blisters, pitting and deformation were evaluated. Figure 5 shows a chrome-plated specimen with rainbow colors.

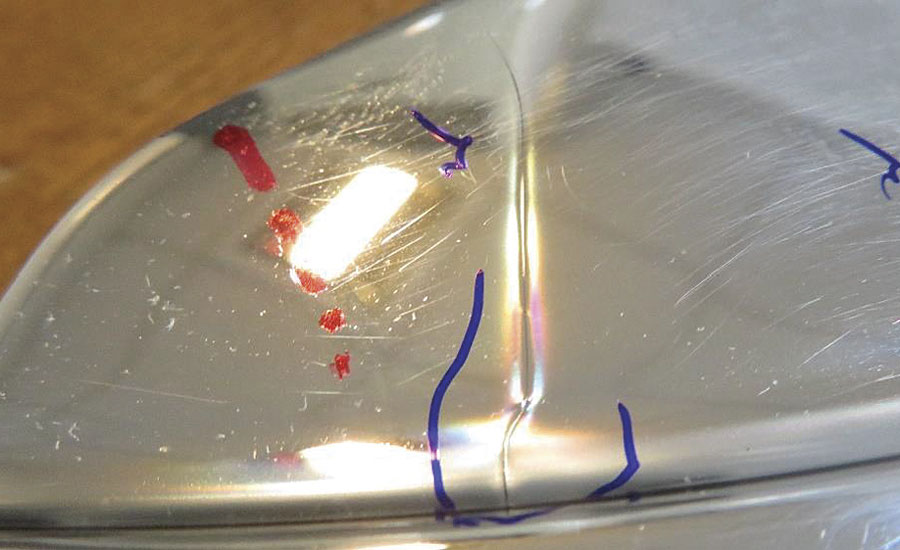
The PVD coated with aluminum faced defects during the test such as deformation, stress cracking, blistering and blackish coating, which be seen in Figures 6-8.
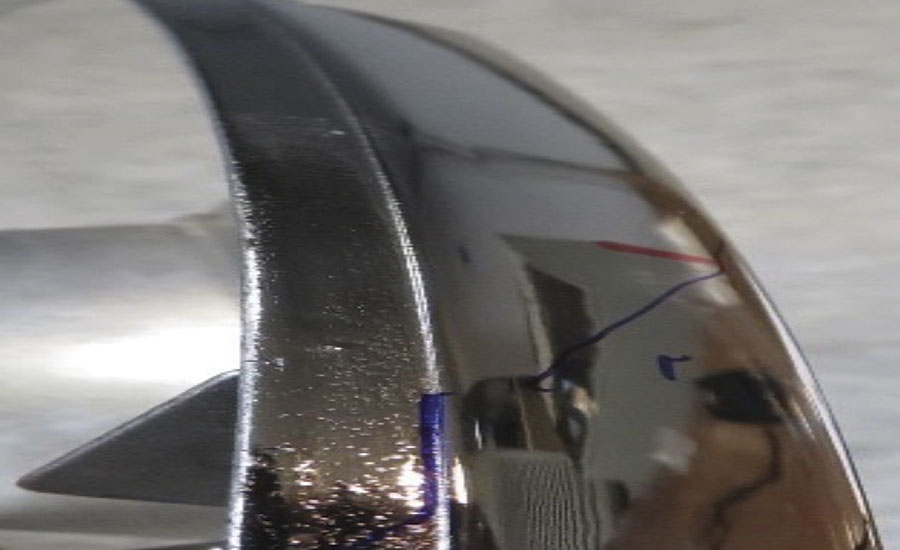
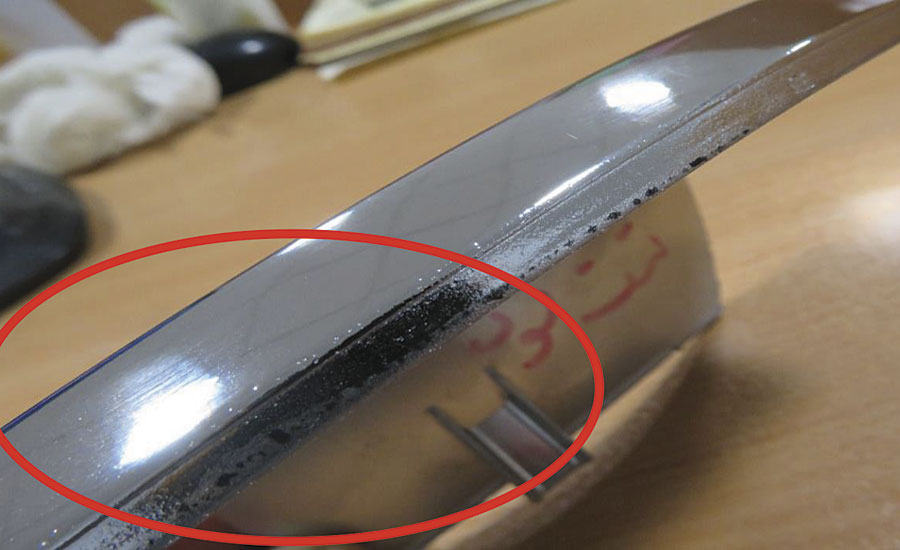



Humidity Resistance
The PVD-coated specimen was placed in a humidity chamber for 30 days with 95%-100% humidity at 35 °C. Results are shown in Figure 9.
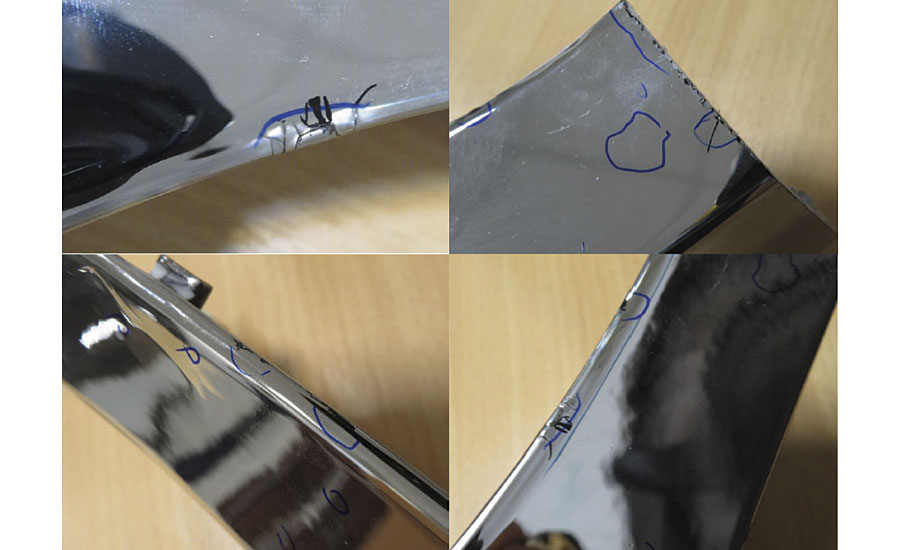

FIGURE 9 ? PVD coating demolished, cracking and with black side defect.
Salt Spray Test Method
Salt spray testing should be done to evaluate a coating’s resistance to corrosion. All of the ABS plastic parts were tested with the CASS standard method for 120 hrs (Figure 10).
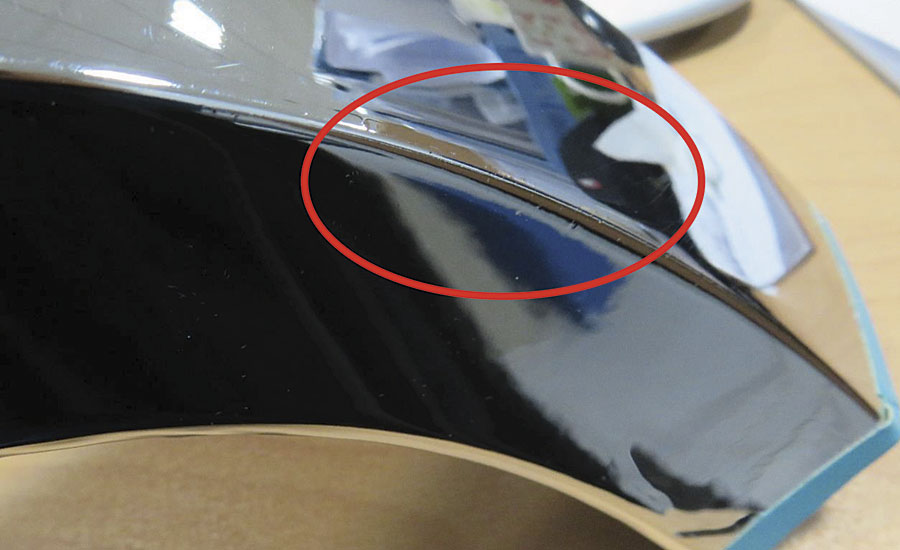

According to the test results, the PVD coating through aluminum target without a UV-curing system compared with chrome plating has some advantages and disadvantages, as discussed below:
PVD coating has a minimum thermal resistance during the thermal cycle test;
Humid environments cause a black side defect on the coating;
There was adhesion loss, making the surface susceptible to scratches;
The PVD coating showed a negative resistance to soluble alkalis found in detergent materials. Based on this test, the coating was completely removed, however the chrome-plated coating had a high resistance in the alkali environment.

Scan and pay attention to the public number